What is the difference between the low FODMAP diet and gluten free diet?
What are the diets for? What are their similarities and differences? Continue to read if you have the same questions!

What is a Low FODMAP Diet?
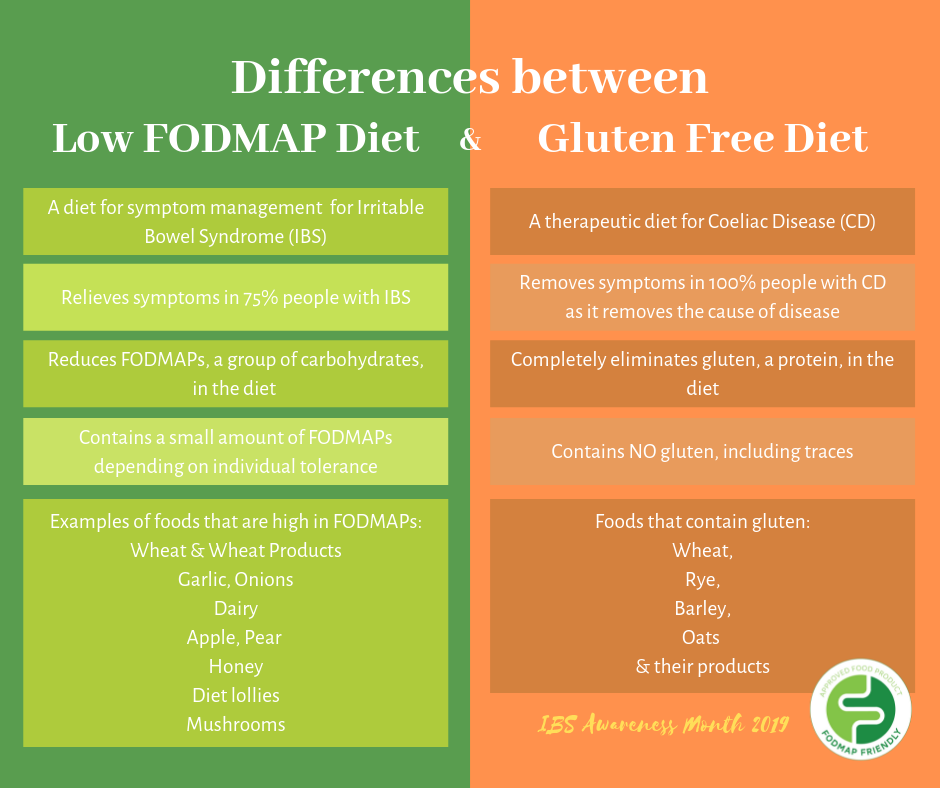
FODMAP stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides And Polyols. They are a group of carbohydrates that can be poorly absorbed in the small intestine and move on to be fermented in the large intestine. The production of gases from the fermentation can trigger symptoms in people with IBS. A diet low in FODMAPs has shown to help relieve symptoms in about 75% of people with IBS.
What is a Gluten Free Diet?
Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye, barley and oats, and their food products. The gluten-free diet is a therapeutic diet for people diagnosed with coeliac disease. In people with coeliac disease, the immune system reacts abnormally to gluten (a protein found in wheat, rye, barley and oats) and causes inflammation and damage to the gut lining. When the small bowel is damaged, nutrients from food aren’t absorbed properly into the body which can cause nutrient deficiency and gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhoea. Eliminating gluten from the diet, i.e. the four grains mentioned above and their products, allows the small bowel lining to heal and symptoms to resolve.
Find out more information about the gluten free diet and coeliac disease with this infographic.
What are the similarities between the two diets?
The foods that should be avoided in both diets overlap because the main grains that contain gluten (wheat, barley, and rye) are also high in FODMAPs! That means, when you are following a gluten free diet, you are cutting out some FODMAP containing grains too.
What are the differences between the two diets?
The following image summarizes the key differences between the low FODMAP diet and the gluten free diet.
Why do some people find that cutting out gluten from the diet helps relieve their IBS symptoms?
As mentioned above, the main grains that contain gluten (wheat, barley, and rye) are also coincidentally high in FODMAPs, mainly oligosaccharides and excess fructose. Hence, when you are following a gluten free diet, you are cutting out some FODMAPs too. If you have IBS and are sensitive to these particular subgroups of FODMAPs present in these grains, you may experience some symptom relief from eating these grains that are gluten free. However, it is important to note that not all gluten free foods are low FODMAP. Many gluten free products contain high FODMAP ingredients such as soy flour, coconut flour, lentil flour and besan (chickpea) flour.
To be sure that the gluten free product is also low in FODMAPs, look for the FODMAP Friendly logo on the packet or consult your dietitian.